 --fast-version-control
--fast-version-control
Concept
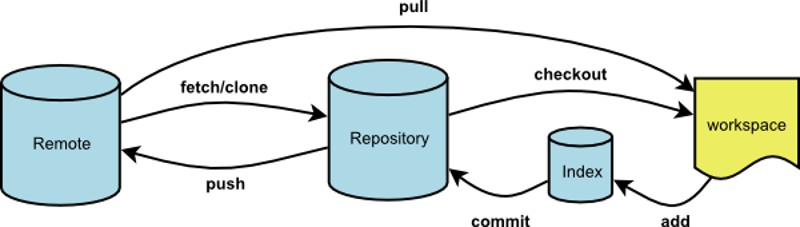
仓库结构
git仓库信息包含本地仓库(Repository)和远程仓库(remote),两者具有相同结构。
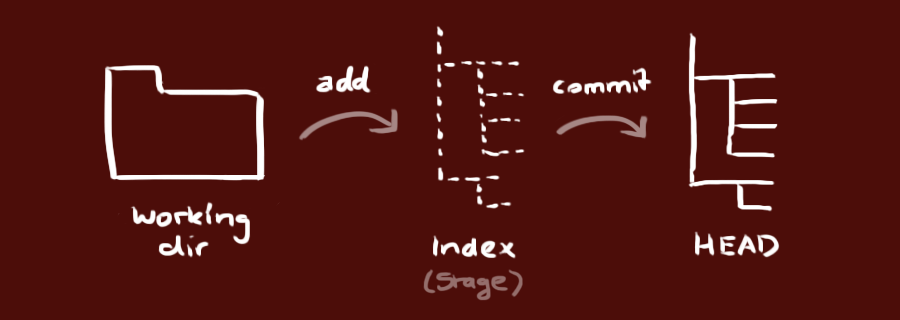
Your local repository consists of three "trees" maintained by git:
-
Working Directory: which holds the actual files (file system);
-
Index: which acts as a staging area;
Git uses its hash algorithm to index everything in your repo. Each file has a SHA that reflects the contents of that file. Each directory, in turn, is hashed. If a file in that directory changes, then the SHA of the directory changes too.
-
HEAD: which points to the last commit you've made.
Each commit contains the SHA of the top-level directory in your repo along with some other info.
由于远程仓库可能由多人参与维护,因此其版本与本地仓库版本(HEAD)可能不同。因此,将本地仓库推送到远程之前,需要首先将远程仓库拉取(fetch)到本地,并保证本地提交版本未落后于远程版本。否则,需要暂存本地更改,并使用远程版本更新本地版本,再恢复本地更改后提交。强制提交本地落后的版本可能会产生文件内容冲突。
repository
alias
bookmark
Workflow
Operations
stage
commit
使用git的原则
-
Only put source files into version control, never generated files.
-
Commit binary files with caution and strongly avoid committing large files.
-
never put confidential information into a repo, especially one you might share publicly.
Status
tracked/un-tracked
modified
staged/un-staged
committed
安装git
git配置
git config --global init.defaultBranch <name>
git config --global --edit # 打开git配置文件并编辑
添加--global将设置应用于当前系统用户下的所有仓库的默认配置。
配置文件位置
| 选项 | 说明 | 配置文件路径 |
|---|---|---|
--system | 默认配置 | /etc/gitconfig |
--global | 用户全局配置 | ~/.gitconfig or ~/.config/git/config |
--local | 仓库配置 | .git/config |
列出所有配置:
git config -l,--list
.gitignore:声明忽略仓库目录下的未追踪文件。
git用户配置
使用git提交代码前需要配置git用户信息(用户名和邮箱)。
git config user.name "John Doe"
git config user.email "you@emal.com"
输出格式配置
git config color.ui true # 使用彩色输出
git config color.ui auto
git图形界面
gitk
管理仓库
创建仓库
git init [project-name] # 默认在当前目录下创建仓库
git clone [url] [local_path]
在远程服务器创建仓库:
git remote add origin <server>
查看状态
列出仓库目录下的待提交的已更改文件以及未加入仓库的新文件。
git status [-s | --short]
-s:输出简洁信息。
对比文件的更改:
git diff [--staged | --cached] [file]
图形用户界面。
git difftool [--tool-help]
记录
查看当前分支的历史记录
git log --author=bob --pretty=oneline
git log --name-status # 显示修改过的文件名
git log --graph --oneline --decorate --all # 查看分支树
git show [commit]
管理仓库内容
添加文件
将未加入仓库的文件加入仓库以追踪更改;或者将已加入仓库的文件暂存(stage)等待提交(commit)。
git add -i [file/dir] # 'git add .' adding the current directory
-i:交互式添加文件。
Marking merge-conflicted files as resolved.
编辑文件
直接使用文件系统命令移动文件,git可能无法检测重命到移动行为(可能任务先删除一个文件并创建另一个文件)。使用git mv更改文件名(移动文件):
git mv [file-original] [file-renamed]
如果被改名的文件已经做了修改,则修改和重命名记录都能被保留。
优先提交(commit)文件名修改。
移除文件
从仓库中移除文件。
git rm [-rf][--cached][file]
-f:如果一个文件被修改过,则需要-f选项强制移除。该选项避免了意外数据丢失。
--cached:保留本地文件。
提交更改
将本地仓库的更改保存为本地的最新版本(HEAD)。
git commit [options] [files]
==默认提交暂存的文件==,如果命令列出文件,则忽略现阶段暂存的文件,直接提交列出的文件。
-m 'message':提交信息。未提供选项则默认会弹出文本编辑器保存提交信息。--dry-run:列出提交的概览信息而不执行提交。--amend:追加内容,替换之前的提交(而不产生新的commit ID)。-a: 直接将所有修改过的已追踪的(包括未暂存的)文件提交,删除所有从工作树移除的文件。--interactive: 交互式决定每个文件是否要提交。
最小化提交代码原则:每次提交包含单一的问题修复、功能更新,从而便与按主题追踪代码更改。
提交信息书写规范
推送更改
git push origin <branch> # 默认分支为master
如果本地仓库并非从远程复制过来,则需要首先连接到远程服务器:
git remote add origin <server>
替换本地修改
用最近提交版本还原工作目录下修改过的文件:
git checkout -- <filename>
其他文件的修改不会受影响。
用服务器的版本替代本地的==修改和提交==:
git fetch origin
git reset --hard origin/master
--hard:删除所有比加载版本新的版本。
过滤仓库内容
忽略已经提交到仓库的文件的最新更改:
git update-index --assume-unchanged <file>
停止忽略:
git update-index --no-assume-unchanged <file>
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/vsts/git/tutorial/ignore-files?view=vsts&tabs=visual-studio
显示忽略的文件:
git ls-files --other --ignored --exclude-standard
分支(Branching)
如果有多项功能需要并行开发,可以使用分支来管理代码的多个版本。当功能开发测试完成,再将该分支合并回主线版本(master)。
Branches are used to develop features isolated from each other. The
masterbranch is the "default" branch when you create a repository. Use other branches for development and merge them back to the master branch upon completion.新增或修改功能在分支进行,待测试完成后合并到主线版本;Bug修复在主线版本进行。
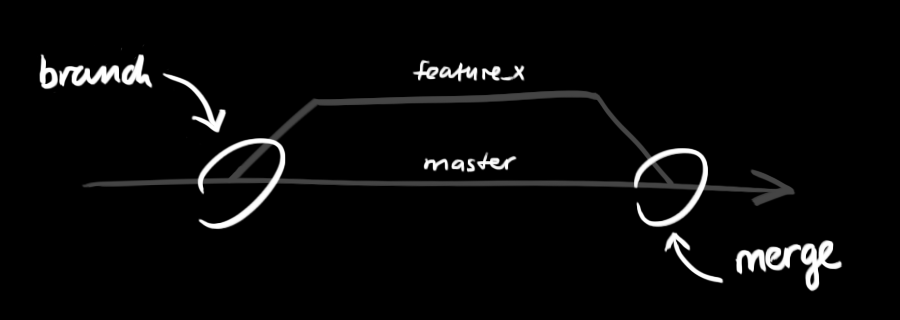
创建分支
从当前状态创建并切换到一个新的分支feature_x:
git checkout -b feature_x
do commit before checkout to avoid data loss.
仅创建分支:
git branch [old_branch] new_branch # 默认从当前分支创建分支
仅切换分支:
git checkout <branch_name> # e.g. master
为了使分支在远程仓库可用,需要将分支推送到远程仓库。
分支信息
列出分支:
git branch [--list]
删除分支
删除一个分支。
git branch -d,--delete feature_x
更新与合并
获取远程仓库内容(稍后手动合并):
git fetch # 仅更新本地HEAD,不合并工作目录
获取远程仓库内容,并与本地分支/工作目录合并:
git pull [url] [branch] # fetch + merge
当前目录下有更改而未保存时,不能使用远程目录覆盖当前内容,否则当前内容被远程覆盖导致数据丢失。如果直接尝试执行git merge或直接执行git pull将产生错误。为了将远程更新与本地更改合并:
- 使用
git stash [push]命令暂存本地更改,使本地index状态最新; - 然后使用
git pull或git merge将远程与本地仓库合并; - 然后
git stash pop恢复本地更改,待本地工作完成后再将本地更改提交到仓库。
暂存最近更改:
git stash push -m,--message <message>
需要预先配置用户身份。
git stash list # 列出暂存的更改版本
git stash show [id] # 列出对应版本和当前状态的变更信息
git stash pop # 恢复最近更改
git stash drop # 丢弃最近更改(需要先暂存)
如果本地提交和远程提交本版不同:
hint: You have divergent branches and need to specify how to reconcile them.
hint: You can do so by running one of the following commands sometime before
hint: your next pull:
hint:
hint: git config pull.rebase false # merge (the default strategy)
hint: git config pull.rebase true # rebase
hint: git config pull.ff only # fast-forward only
分支合并
将当前分支与另一个分支合并:
git merge <branch>
合并工具:
git mergetool
冲突与消除
git尝试自动合并,当通常会产生冲突。用户需要手动编辑冲突文件来消除冲突。手动编辑完成后,使用:
git add <conflicted_file>
以确认完成合并。在开始合并前,可以对比两个分支:
git diff <source_branch> <target_branch>
https://git-scm.com/docs/git-mergetool
https://git-scm.com/docs/git-merge
发布
tagging
git tag 1.0.0 <short_commit_id> # commit id 前10位
GitHub
GitLab
Squash and merge (FREE)
As you work on a feature branch, you often create small, self-contained commits. These small commits help describe the process of building a feature, but can clutter your Git history after the feature is finished. As you finish features, you can combine these commits and ensure a cleaner merge history in your Git repository by using the squash and merge strategy.
- Small commits are joined together, making it simpler to revert all parts of a change.
- When the single commit merges into the target branch, it retains the full commit history.
- Your base branch remains clean, and contains meaningful commit messages.
Each time a branch merges into your base branch, up to two commits are added:
- The single commit created by squashing the commits from the branch.
- A merge commit, unless you have enabled fast-forward merges in your project. Fast-forward merges disable merge commits.
By default, squashed commits contain the following metadata:
- Message: Description of the squash commit, or a customized message
- Author: User that created the merge request
- Committer: User who initiated the squash
Project owners can create new default messages for all squash commits and merge commits.
角色与权限管理
分支合标签保护
设置参与人员修改分支的权限。
[Branch]
branch="master*"
allow to merge="Maintainers"
allow to push="Developers+Maintainers"
[Tag]
tag="v-*"
allow to create="Maintainers"